A special city (特例市, Tokureishi) of Japan was a category of cities in Japan in operation until 2015. Each special city had a population of at least 200,000, and was delegated functions[specify] normally carried out by prefectural governments. Those functions were a subset of the functions that were delegated to core cities.
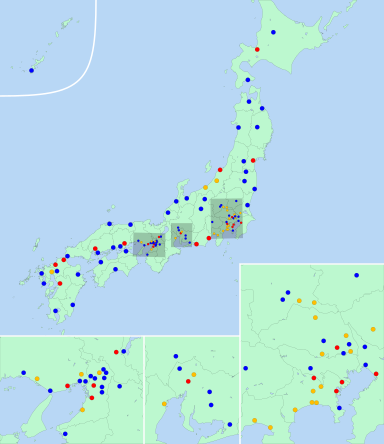
■ ― Designated cities
■ ― Core cities
■ ― Special cities
The category of special cities was established by the Local Autonomy Law, article 252 clause 26. They were designated by the Cabinet after a request by a city council and a prefectural assembly.
Because the level of autonomy delegated to special cities was similar to that for core cities, after consultation with local governments the category of special cities was abolished in the revision of the Local Autonomy Act enacted on April 1, 2015. Cities with a population of at least 200,000 may now apply to be directly promoted to core city status. Special cities that have not been promoted may still retain autonomy, and are called special cities for the enforcement period (施行時特例市, Shikōji Tokurei shi), but this is regarded as a temporary arrangement. [1]
The special cities were not the same as the special wards of Tokyo. They were also different from the special (designated) cities (特別市, tokubetsu-shi) that were legally established under the Local Autonomy Law between 1947 and 1956, in an arrangement that was never implemented. They would have been prefecture-independent cities (in an analogous way, special wards are city-independent wards). They were the legal successors to the 1922 "six major cities" (roku daitoshi; only five were left in 1947 as Tokyo City had been abolished in the war) and precursors to the 1956 designated major cities that have expanded autonomy, but not full independence from prefectures.[2]
List of special cities
editAs of 2015, when the category was abolished, 23 cities had been designated special cities:
| Name | Japanese | Flag | Emblem | Area (km2) | Population (2012) | Date of designation | Region | Prefecture | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atsugi | 厚木市 | 93.83 | 224,181 | 2002-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa | |||
| Chigasaki | 茅ヶ崎市 | 35.71 | 239,874 | 2003-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa | |||
| Fuji | 富士市 | 244.95 | 245,015 | 2001-04-01 | Chūbu | Shizuoka | |||
| Hiratsuka | 平塚市 | 67.88 | 260,061 | 2001-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa | |||
| Ibaraki | 茨木市 | 76.52 | 276,474 | 2001-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka | |||
| Isesaki | 伊勢崎市 | 139.44 | 207,253 | 2007-04-01 | Kantō | Gunma | |||
| Jōetsu | 上越市 | 973.81 | 202,366 | 2007-04-01 | Chūbu | Niigata | |||
| Kakogawa | 加古川市 | 138.51 | 268,175 | 2002-04-01 | Kansai | Hyōgo | |||
| Kasugai | 春日井市 | 92.78 | 306,573 | 2002-04-01 | Chūbu | Aichi | |||
| Kasukabe | 春日部市 | 66.00 | 236,976 | 2008-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama | |||
| Kishiwada | 岸和田市 | 72.68 | 197,629 | 2002-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka | |||
| Kumagaya | 熊谷市 | 159.82 | 201,814 | 2009-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama | |||
| Nagaoka | 長岡市 | 891.06 | 281,101 | 2007-04-01 | Chūbu | Niigata | |||
| Numazu | 沼津市 | 186.96 | 199,883 | 2000-04-01 | Chūbu | Shizuoka | |||
| Odawara | 小田原市 | 113.79 | 194,672 | 2000-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa | |||
| Ōta | 太田市 | 175.54 | 217,107 | 2007-04-01 | Kantō | Gunma | |||
| Saga | 佐賀市 | 431.84 | 237,501 | 2014-04-01 | Kyushu | Saga | |||
| Sōka | 草加市 | 27.46 | 244,851 | 2004-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama | |||
| Takarazuka | 宝塚市 | 101.89 | 227,617 | 2003-04-01 | Kansai | Hyōgo | |||
| Tokorozawa | 所沢市 | 72.11 | 344,194 | 2002-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama | |||
| Tsukuba | つくば市 | 283.72 | 244,528 | 2007-04-01 | Kantō | Ibaraki | |||
| Yamato | 大和市 | 27.09 | 230,357 | 2000-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa | |||
| Yokkaichi | 四日市市 | 206.44 | 306,107 | 2000-04-01 | Chūbu | Mie |
References
edit- ^ 日本總務省 - 中核市・施行時特例市. soumo.go.jp.
- ^ Satoru Ohsugi (2011): The Large City System of Japan Council of Local Authorities for International Relations and Institute for Comparative Studies in Local Governance, National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies. – Note: this paper translates tokurei-shi as "special case city" and uses "special city" for tokubetsu-shi
External links
edit- "Japan's Evolving Nested Municipal Hierarchy: The Race for Local Power in the 2000s," by A.J. Jacobs at Urban Studies Research, Vol. 2011 (2011); doi:10.1155/2011/692764
- "Large City System of Japan"; graphic shows special cities compared with other Japanese city types at p. 1 [PDF 7 of 40]
- "Growth in Second Tier Cities - Urban Policy Lessons from Japan" briefing by CLAIR London on classes of Japanese cities (PDF)