Portal:Viruses
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!

Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Smallpox is an eradicated infectious disease of humans caused by the Variola major and V. minor viruses. V. major causes a serious disease with a mortality rate of around 30%; V. minor is associated with much milder symptoms and mortality below 1%. The virus is mainly transmitted by the respiratory route but can also be carried on contaminated objects. Smallpox preferentially infects skin cells, resulting in a usually maculopapular rash, and later, raised fluid-filled blisters. Most V. major survivors have permanent scarring, commonly on the face, which can be extensive. Less common long-term complications include blindness resulting from corneal ulceration and scarring, and in young children, limb deformities due to arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Smallpox probably emerged in human populations in about 10,000 BC; the mummified body of Egyptian pharaoh Ramses V shows evidence of smallpox rash. The disease was responsible for an estimated 300–500 million deaths during the 20th century. Smallpox vaccine, the earliest vaccine, was developed in the 18th century. After intensive vaccination campaigns, the last natural infection occurred in 1977. Smallpox was certified the first infectious disease to be eradicated globally in 1979. Debate is ongoing over whether all stocks of the virus should be destroyed.
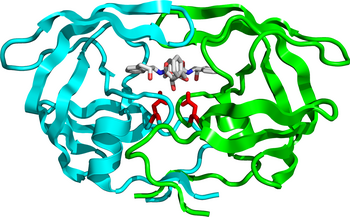
Selected image
An HIV protease inhibitor (white) bound to its target, the HIV-1 protease (blue and green). The viral enzyme is a dimer of two identical subunits with the active site (red) in the cleft between them.
Credit: Boghog (28 June 2008)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
Infectious diseases are symptomatic diseases of an individual host resulting from the infection and replication of pathogens, including viruses, prions, bacteria, fungi, protozoa and multicellular parasites. Infectious diseases were responsible for 17% of human deaths globally in 2013, with HIV, measles and influenza being among the most significant viral causes of death.
Infectious pathogens must enter, survive and multiply within the host, and spread to fresh hosts. Relatively few microorganisms cause disease in healthy individuals, and infectious disease results from the interplay between these rare pathogens and the host's defences. Infection does not usually result in the host's death. The pathogen is generally cleared from the body by the host's immune system, although persistent infection occurs with several viruses. Transmission can occur by physical contact, contaminated food, water or objects, body fluids, airborne inhalation or via vectors, such as the mosquito (pictured). Diagnosis sometimes involves identifying the pathogen; techniques include culture, microscopy, immunoassays and PCR-based diagnostics.
Selected outbreak
In the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak, the first cases of the newly emerged SARS coronavirus were reported in November 2002 from the Chinese Guangdong province. The virus soon spread across Asia, with China, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Singapore being the worst affected countries; a secondary outbreak occurred in Canada. The rapid initial spread of the outbreak has been in part attributed to China's slow response to the early cases. Over 8,000 people were infected, with a case fatality rate of 11%. Those over 65 years had a much higher mortality rate, greater than 55%. The outbreak was contained by July 2003, and no cases have been reported since 2004.
At the time of the outbreak, the immediate source of SARS coronavirus was thought to have been the masked palm civet (Paguma larvata; pictured), which was sold as food in Guangdong markets. The virus was also found in raccoon dogs, ferret badgers and domestic cats. More recent research has suggested that the natural reservoir could be horseshoe bats.
Selected quotation
| “ | ...in a flash I had understood: what caused my clear spots was, in fact, an invisible microbe, a filterable virus, but a virus parasitic on bacteria. | ” |
—Félix d'Herelle on the discovery of bacteriophages
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are two small DNA viruses in the Dependoparvovirus genus of the Parvoviridae family. They cannot complete their lytic replication cycle without a helper virus, which include adenoviruses, herpesviruses and vaccinia. In the absence of the helper, AAVs can integrate into the host genome at a specific site on human chromosome 19, or persist as an episome. The 20 nm icosahedral capsid lacks an envelope, and contains a single-stranded DNA genome of around 4.7 kb. AAVs infect humans and some other primates without causing disease. They generate only a mild immune response, including neutralising antibodies. The best-studied of the 11 serotypes, AAV-2, infects nerve cells, liver cells, skeletal muscle and vascular smooth muscle, using heparan sulphate proteoglycan as its primary receptor.
Its low pathogenicity makes AAV an attractive basis for viral vectors for gene therapy. Alipogene tiparvovec to treat lipoprotein lipase deficiency was the first gene therapy to be licensed, but was later withdrawn. Promising results have been obtained in early clinical trials with AAV-based gene therapy in haemophilia, congestive heart failure, spinal muscular atrophy, Parkinson's disease and the rare eye disease Leber congenital amaurosis.
Did you know?
- ...that elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus, found mostly among young captive Asian elephants (pictured), can have a fatality rate of up to 90%?
- ...that epidemiologist Joseph L. Melnick found that polio chiefly spread through fecal contamination, usually by soiled hands, and that the poliovirus could survive for extended periods in sewage?
- ...that a global advisory committee has been monitoring rapidly developing COVID-19 vaccines against a background of growing misinformation and vaccine hesitancy?
- ...that sexual-health doctor Mags Portman and activist Greg Owen worked together to provide accessible HIV medication, preventing thousands of new HIV diagnoses in the United Kingdom?
- ...that before the Hershey–Chase experiment confirmed the role of DNA, scientists believed that genes were carried by proteins?
Selected biography
Edward Jenner (1749–1823) was an English physician and scientist who pioneered the smallpox vaccine, the world's first vaccine. Noting the common observation that milkmaids were generally immune to smallpox, Jenner postulated that the pus in the blisters that milkmaids received from cowpox (a similar but much less virulent disease) protected them from smallpox. In 1796, Jenner tested his hypothesis by inoculating an eight-year-old boy with pus from an infected milkmaid. He subsequently repeatedly challenged the boy with variolous material, then the standard method of immunisation, without inducing disease. He published a paper including 23 cases in 1798. Although several others had previously inoculated subjects with cowpox, Jenner was the first to show that the procedure induced immunity to smallpox. He later successfully popularised cowpox vaccination.
Jenner is often called "the father of immunology", and his work is said to have saved more lives than that of any other individual.
In this month
1 December 1988: First World AIDS Day
4 December 1915: Frederick Twort discovered bacteriophages
4 December 2009: New order of single-stranded RNA viruses, Tymovirales, announced
6 December 1995: Saquinavir approved by FDA; the first HIV protease inhibitor
6 December 2013: Sofosbuvir approved for treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV), the first HCV nucleotide analogue and the first drug approved for interferon-free treatment
9 December 1979: Global Commission for Certification of Smallpox Eradication signed document formally certifying smallpox eradication
15 December 1955: Crystallisation of poliovirus by Fred Schaffer and Carlton Schwerdt, the first animal virus to be crystallised
15 December 1967: Infectious phi X 174 synthesised by Arthur Kornberg and coworkers, the first synthetic virus
18 December 1908: Poliovirus discovered by Karl Landsteiner and Erwin Popper
25 December 1982: Lambda phage (plaques pictured) sequenced by Fred Sanger and coworkers
28 December 1936: Scrapie shown to be transmissible, the first demonstration for a prion disease
29 December 1926: Thomas Milton Rivers proposed that viruses are obligate parasites
Selected intervention
Several human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines, including Cervarix and Gardasil, have been approved to protect against infections with particular types of HPV, associated with cervical and other cancers. All vaccines protect against the high-risk HPV types 16 and 18. Gardasil is a quadrivalent vaccine that additionally protects against low-risk HPV-6 and -11, which are associated with most cases of genital warts. A second-generation nine-valent Gardasil vaccine protects against five additional high-risk HPV types. It is estimated that the vaccines may prevent 70% of cervical cancer, 80% of anal cancer, 60% of vaginal cancer, 40% of vulvar cancer and possibly some oropharyngeal cancers. Protection lasts for at least 8–9 years. Some advocate giving Gardasil to men and boys with the primary aim of protecting their female sexual partners; others consider vaccinating only women and girls to be more cost effective. The licensed vaccines are subunit vaccines, containing only the L1 capsid protein of the virus, which self-assembles into virus-like particles. They are not effective in people already infected with HPV. Research is ongoing into therapeutic HPV vaccines including the viral oncoproteins, E6 and E7, but none has yet been licensed.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus