Trigonometric Functions, often simply called trig functions, are mathematical functions that relate the angles of a right triangle to the ratios of the lengths of its sides.
Trigonometric functions are the basic functions used in trigonometry and they are used for solving various types of problems in physics, Astronomy, Probability, and other branches of science. There are six basic trigonometric functions used in Trigonometry which are:
Six Trigonometric Functions
The image added below shows a right angle triangle PQR.
-(1).png)
Then the six basic trigonometric functions formulas for this right angle triangle is,
- sin θ = Perpendicular/Hypotenuse = PQ/PR
- cos θ = Base/Hypotenuse = QR/PR
- tan θ = Perpendicular/Base = PQ/QR
- sec θ = Hypotenuse/Base = PR/PQ
- cosec θ = Hypotenuse/Perpendicular = PR/QR
- cot θ = Base/Perpendicular = QR/PQ
Values of Trigonometric Functions
Value of trigonometric functions can easily be given using the trigonometry table. These values of the trigonometric functions are very useful in solving the various trigonometric problems. The required trigonometry table is added below:
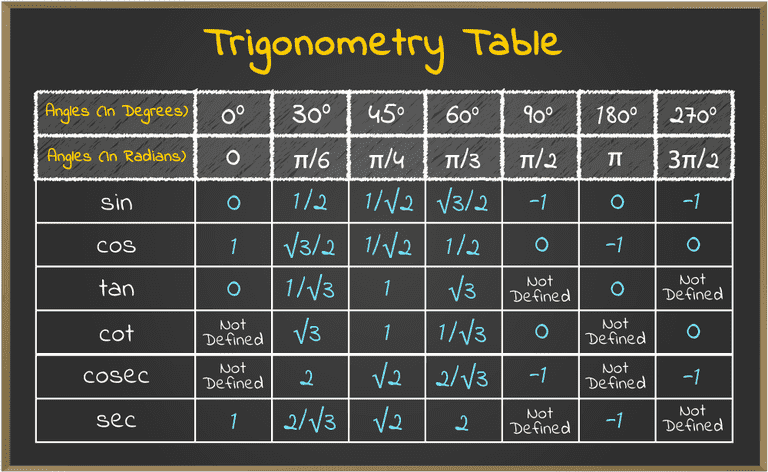
The table added below shows all the values of the important angles from 0 to 180 degrees for all the trigonometric functions.
Trigonometric Functions in Four(4) Quadrants
The trigonometric functions are the periodic functions and their value repeat after a certain interval. Also, not all the trigonometric functions are positive in all the quadrants.
We divide the cartesian space into four quadrants namely, I, II, III and IV quadrants, and the value of the trigonometric functions whether they are positive or negative in each quadrant is given as,
- I Quadrant: All Positive
- II Quadrant: sin θ and cosec θ Positive
- III Quadrant: tan θ and cot θ Positive
- IV Quadrant: cos θ and sec θ Positive
Image explaining the same is added below:
.png)
Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions graphs plots the value of the trigonometric functions for different values of the angle(θ). For some the trigonometric functions are bounded as,
- Trigonometric functions sin θ and cos θ are bounded between – 1 and 1 and to their graphs oscillates between -1 and 1 on the y-axis.
- Graph of the trigonometric function tan θ, and cot θ has a range from negative infinity to positive infinity.
- Graph of the trigonometric function sec θ, and cosec θ has a range from negative infinity to positive infinity excluding (-1, 1).
Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
Suppose we have a trigonometric function f(x) = sin x, then the domain of the function f(x) is all the values of x that the function f(x) can take, and the domain is all possible outcome of the f(x). The domain and range of all the six trigonometric functions are:
|
Trigonometric Function
|
Domain
|
Range
|
| sin x |
R |
[-1, +1] |
| cos x |
R |
[-1, +1] |
| tan x |
R – (2n + 1)π/2 |
R |
| cot x |
R – nπ |
R |
| sec x |
R – (2n + 1)π/2 |
(-∞, -1] U [+1, +∞) |
| cosec x |
R – nπ |
(-∞, -1] U [+1, +∞) |
Properties of Trigonometric Functions
Some of the common properties of trigonometric functions are discussed below:
Period refers to the length of one complete cycle of a trigonometric function, after which the function repeats.
- Sine (sin), Cosine (cos), Secant (sec), Cosecant (csc): Period = 2π
- Tangent (tan), Cotangent (cot): Period = π
Symmetry refers to the property that describes how the function behaves under reflection, translation, or rotation.
Derivative of Trigonometric Functions
Differentiation of trigonometric function can be easily found and which the slope of that curve for that specific value of the trigonometric functions. The differentiation of all six trigonometric functions are added below:
- d/dx (sin x) = cos x
- d/dx (cos x) = -sin x
- d/dx (tan x) = sec2x
- d/dx (cot x) = -cosec2x
- d/dx (sec x) = sec x tan x
- d/dx (cosec x) = -cosec x cot x
Integration of Trigonometric Functions
As integration of any curve gives the area under the curve, the integration of trigonometric function also give the area under the trigonometric function. The integration of various trigonometric functions are added below.
- ∫ cos x dx = sin x + C
- ∫ sin x dx = -cos x + C
- ∫ tan x dx = log|sec x| + C
- ∫ cot x dx = log|sin x| + C
- ∫ sec x dx = log|sec x + tan x| + C
- ∫ cosec x dx = log|cosec x – cot x| + C
Some other important trigonometric integrals are:
- ∫ sec2x dx = tan x + C
- ∫ cosec2x dx = -cot x + C
- ∫ sec x tan x dx = sec x + C
- ∫ cosec x cot x dx = -cosec x + C
Next Article: Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions.
Trigonometric Functions-FAQs
What are Trigonometric Functions in Maths?
Trigonometric Functions are the function used in trigonometry these functions gives the relation between, the angles and the sides of the triangle.
What are Six Basic Trigonometric Functions?
The six trigonometric functions are,
- sin x
- cos x
- tan x
- cosec x
- sec x
- cot x
What are Pythagorean Identities of Trigonometric Function?
Pythagorean Identities of Trigonometric Function are,
- sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
- 1 + tan2θ = sec2θ
- 1 + cot2θ = cosec2θ
What are Inverse Trigonometric Functions?
Inverse Trigonometry Functions as the name suggest are the inverse of the trigonometric functions. We can explain this as suppose,
sin x = a
Then inverse of sin function is sin-1 and its value is defined as,
sin-1(a) = x
Similarly, inverse function of all the trigonometric functions can be easily calculated.
What are Applications of Trigonometric Functions?
Trigonometric functions are very useful and they are used in various branches of mathematics, and physics for various purposes. They are used in Coordinate Geometry, Complex Analysis, etc. They are also used in Astronomy, Wave Physics, etc.
What is Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions?
Domain of a trigonometric function is the value of θ for which the function has a real value.
Range of a trigonometric Function is the interval in which the value of the trigonometric function exists.
Is it Important to study Trigonometric Functions for Class 11?
Yes, Trigonometric Functions is very important for Class 10 as well as Class 11 Students. As it forms a base to study other units including Calculus and Geometry.
What are 3 Basic Trig Function?
The three basic trig functions are,
- Sine Function (sin x)
- Cosine Function (cos x)
- Tangent Function (tan x)