What is Iterative Design?
Last Updated :
26 Jul, 2024
Iterative design is a process where designers continuously improve a product by repeating cycles of testing and refining. This method helps create user-friendly and high-quality products by allowing designers to identify and fix issues early on. By involving users in each step, iterative design ensures that the final product meets their needs and preferences. It's a flexible and efficient way to develop websites, apps, and other digital products.
What is Design Iteration?
Iterative design is a process where designers continuously improve a product through repeated cycles of testing and refining. This method involves creating a basic version of the product, testing it with users, gathering feedback, and making necessary improvements. By repeating this cycle, the design gradually gets better and more effective. Iterative design is essential for creating high-quality, user-friendly products, ensuring they meet user needs and provide an excellent user experience (UX). This approach is widely used in UI design to achieve the best possible results.
Why Do We Need Design Iteration?
Design iteration is crucial for several reasons, especially when aiming for high-quality, user-friendly products. Here’s why it’s important:
1. User-Centric Design
- Focus on User Needs: By involving users throughout the design iterations, you ensure that the final product effectively meets their needs and preferences. This user-centric approach leads to better user satisfaction and usability.
2. Enhancing Functionality
- Improving Reliability: Iterative design allows teams to identify and fix potential issues early on. By continuously refining the design, you can create a more reliable and functional final product that performs well.
3. Adaptability to Change
- Responding to Trends: In fast-changing industries, needs and preferences can shift quickly. Iterative design enables designers to adapt to these changes efficiently, ensuring the product remains relevant and up-to-date.
4. Risk Mitigation
- Reducing Errors: Early identification and resolution of problems through iterative testing and refinement reduce the risk of costly errors in the final product. This proactive approach saves time and resources in the long run.
Iterative Design Process Model
The iterative design process is a cycle of steps that are repeated to improve a design or product. Here’s a simple explanation of each step according to the image:
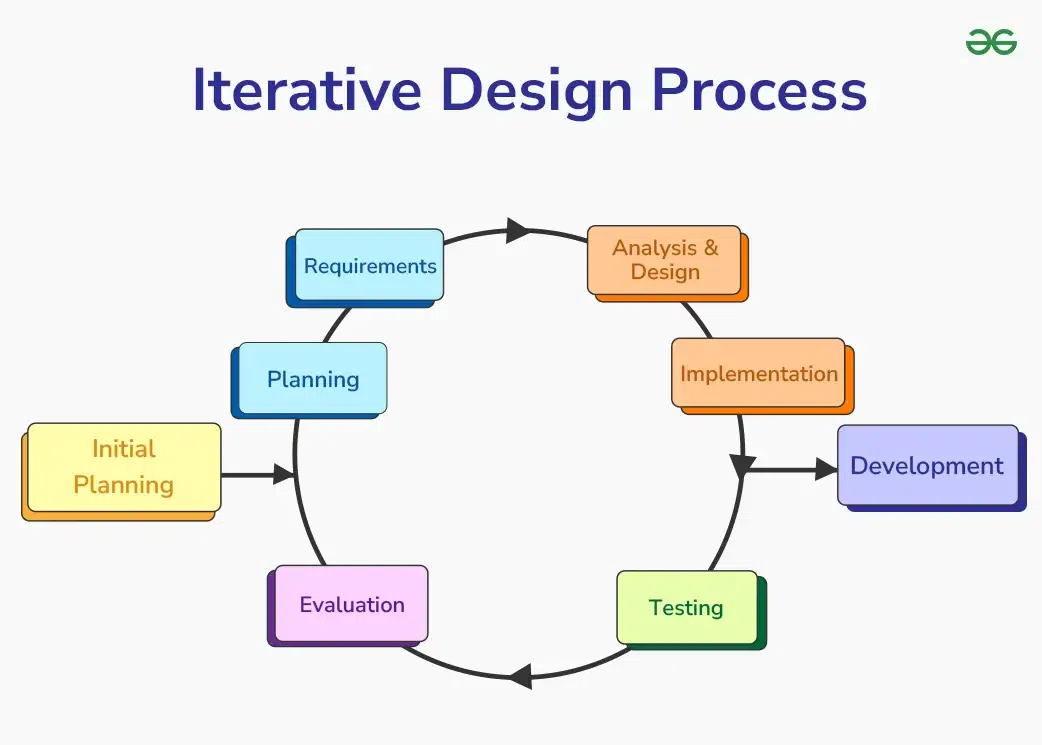 Iterative Design Process Model
Iterative Design Process Model1. Initial Planning
Start by defining the goals and scope of the project. Identify what you want to achieve and outline the basic plan.
2. Requirements
Gather all the necessary requirements for the project. Understand what needs to be done and what resources are needed.
3. Analysis & Design
Analyze the requirements and create a design. Plan how the project will look and work, considering both functionality and aesthetics.
4. Implementation
Develop the design into a working model. This is where the actual building or coding happens.
5. Development
Further develop and refine the working model. Add more details and improve the functionality.
6. Testing
Test the design to make sure everything works correctly. Identify any issues or bugs that need to be fixed.
7. Evaluation
Evaluate the results of the testing. Gather feedback and determine what improvements are needed.
8. Planning
Plan the next iteration based on the evaluation. Adjust the goals and requirements as needed.
Benefits of Iterative Design
Iterative design offers many advantages, making it a popular approach for creating high-quality products. Here are the key benefits:
1. Continuous Improvement
- Ongoing Excellence: Iterative design promotes a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging teams to strive for better results with each version of the product.
2. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- User-Friendly Designs: By incorporating customer feedback into each design iteration, the final product becomes more user-friendly, leading to higher levels of user satisfaction.
3. Cost-Efficiency
- Early Issue Resolution: Addressing problems early in the design phase reduces the likelihood of expensive changes later in the development process, saving time and money.
4. Faster Time to Market
- Speed and Quality: Iterative cycles streamline the design process, allowing products to be launched more quickly without compromising on quality.
Examples of Design Iterations
Design iterations are used in many fields to continuously improve products and ensure they meet user needs. Here are some key examples:
1. Software Development
- Agile Development: Agile methodologies involve continuous feedback loops and iterative progress to ensure the software meets user needs. Each iteration includes planning, development, testing, and review, making the software better with each cycle.
Read More: Agile Software Development – Software Engineering
2. Product Design
- Mobile Phones: The development of smartphones is a great example of design iteration. Each new model builds on existing features and incorporates user feedback to improve functionality, performance, and user experience.
- Automobiles: Car manufacturers use iterative design to enhance safety, efficiency, and user comfort. Each new car model benefits from feedback and technological advancements.
3. Website Design
- User Interface Optimization: Web designers often use iteration to improve user interfaces, making websites easier to navigate and enhancing the overall user experience. This involves testing different layouts, colors, and elements based on user feedback.
- E-commerce Platforms: Online stores frequently update their designs to improve the shopping experience, streamline checkout processes, and boost sales.
4. Video Game Development
- Gameplay Enhancements: Game developers use iterative design to refine gameplay mechanics, graphics, and user interfaces. Player feedback is crucial in this process to ensure a fun and engaging experience.
- Beta Testing: Before the final release, games often go through multiple beta testing phases, where player feedback is used to fix bugs and improve the game.
5. App Development
- Feature Updates: Mobile app developers release regular updates based on user feedback to add new features, improve performance, and fix issues.
- User Experience (UX) Design: Iterative design helps in fine-tuning the user experience by continually testing and refining app interfaces and interactions.
Conclusion
In summary, iterative design is a powerful approach that focuses on continuous improvement and user satisfaction. By repeatedly testing and refining designs, this method helps create reliable, functional, and user-friendly products. Whether you are designing a website, an app, or any other digital product, using iterative design ensures that you deliver high-quality results that meet the needs of your users.
What is Iterative Design - FAQs
What does iterate mean in design?
Iterate in design means to repeatedly test and refine a product to improve it.
What is an iterative style?
An iterative style involves making small, incremental changes and improvements to a design based on feedback and testing.
What is iterative design in GCSE DT?
In GCSE Design and Technology (DT), iterative design is a process of developing and improving a product through repeated cycles of testing and refinement.
What is the iterative UX design process?
The iterative UX design process involves continuously improving the user experience by testing, gathering feedback, and making necessary changes.
What is meant by iterative design?
Iterative design is a method of making gradual improvements to a product by repeatedly testing and refining it.
What are the 5 steps of the iterative design process?
The 5 steps of the iterative design process are: Planning, Designing, Prototyping, Testing, and Refining.
Similar Reads
What is Iterative Design?
Iterative design is a process where designers continuously improve a product by repeating cycles of testing and refining. This method helps create user-friendly and high-quality products by allowing designers to identify and fix issues early on. By involving users in each step, iterative design ensu
6 min read
What is Service Design?
Service Design is a comprehensive approach to enhancing customer experiences by carefully analyzing and optimizing the workflows and tasks involved in delivering a service. Unlike traditional design that focuses solely on the product, service design looks at the entire journey a customer takes, from
8 min read
What is Reflective Design?
Reflective design is a method in software program engineering that emphasizes the dynamic edition and self-modification of software systems primarily based on runtime observations and comments. It involves developing systems that could monitor their very own conduct, examine the surroundings in whic
7 min read
What is Digital Design?
Digital design refers to the. process of designing the interactions and experience of a digital product on any digital device, this digital device could be anything like a mobile phone, a desktop, a tablet, a smartwatch, etc. Your design is responsible for communicating your mission and your product
6 min read
Interactive System Design
Interactive System Design is an Approach to Creating User-friendly and effective Interactive Systems. It always focuses on designing a good User Experience(UX) and User Interface(UI) to ensure that users can interact with the system easily and effectively. Websites, Mobile Applications, and Software
6 min read
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that focuses on understanding users' needs and creating innovative solutions. It involves five key steps: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. By putting the user at the center of the process, design thinking helps teams come up with creative
7 min read
What is Interaction Design Process?
User-centric digital experiences are built on interaction design, which facilitates smooth interactions between people and technology. Designers unearth user demands and behaviors through painstaking research and analysis, which paves the way for intuitive interface design. In order to create interf
6 min read
What is the 3I model in design?
Design thinking frameworks are a great way to ensure that the design team is following a proper design thinking process before you can move on to working on the actual design. The 3I model for design is one such design thinking framework created by IDEO which is a renowned international design firm
6 min read
What Is Usability in Design?
Usability is one of the most important factors that affects the user experience of any application, website, or any other piece of software. Usability principles like Visibility, User control, etc. are make or break for many applications. Usability or user-centered design is the process of designing
5 min read
Iterative Deepening Search (IDS) in AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses various search algorithms to solve problems efficiently. One such algorithm, Iterative Deepening Search (IDS) also known as Iterative Deepening Depth-First Search (IDDFS), combines the advantages of both Depth-First Search (DFS) and Breadth-First Search (BFS)
10 min read
User Interface Design
The user interface is the front-end application view to which the user interacts to use the software. The software becomes more popular if its user interface is: AttractiveSimple to useResponsive in a short timeClear to understandConsistent on all interface screens Types of User InterfaceCommand Lin
7 min read
What is Iteration? - Definition, Meaning & Examples
Iteration is the process of repeating a set of operations or steps. It is like doing something over and over again to make it better. The essence of iteration is cyclical in nature, where each successive repetition (or iteration) is intended to bring one step closer to the final goal or to enhance t
6 min read
What is Product Iteration?
In today’s fast-moving market, focusing on customers is essential. Creating a product isn’t a one-time task, it is about continuously improving it. Product iteration means regularly updating the product based on customer feedback and data. This helps businesses make products that better meet custome
9 min read
What is an Agile Design?
Agile Design is a dynamic and iterative approach rooted in the principles of the Agile methodology, reshaping traditional design practices to enhance collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. Unlike linear processes, Agile Design embraces flexibility, concurrent development, and user-
9 min read
What is an Early Prototype UX Design?
What is an Early Prototype?An early prototype is the preliminary version of a product or a system used to test ideas or functionalities. It is used in the early phases of the development process to quickly and cost-effectively explore design ideas and concepts. They are generally a basic design and
6 min read
What is Circular Design?
Circular design involves designing things with low virgin materials use, long usage in mind, minimizing resource wastage, and reusing most parts or components upon their end-of-life stages. At its core, circular design, which is inspired by the principles of a circular economy, introduces a shift fr
6 min read
Instructional System Design
Instructional System Design (ISD) is a systematic and disciplined approach to growing powerful and efficient educational experiences. ISD presents a structured framework for designing instructional material that facilitates the most fulfilling optimal outcomes. Its number one aim is to enhance the l
8 min read
Why is it important to learn System Design?
In today’s digital world, system design has become an essential skill for software engineers and other professionals working in the tech industry. System design involves the process of designing, developing, and deploying a system that is capable of fulfilling a specific set of requirements. It is a
6 min read
What is Einstellung Effect in Design?
In design which never stops, practitioners are committed to accomplishing the most that their imagination can offer and creating more artworks. On the one hand, designers are always chasing after new solutions and ideas but inevitably they usually end up developing the same cognitive biases that blo
5 min read