Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cells Can Differentiate Into Retinal
- 1. Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells Can Differentiate into Retinal Cells in Injured Rat RetinaBy Anna Begelfer-OstrovskiMinoru Tomita1,2, Yasushi Adachi1,2,3,Haruhiko Yamada2, Kanji Takahashi2,Katsuji Kiuchi2,5, Haruki Oyaizu1, Kazuya Ikebukuro1, Hiroyuki Kaneda1, Miyo Matsumura2,3,4, Susumu Ikehara M.D.1,3,
- 2. Bone marrow-spongy, fatty tissue houses stem cells.located inside a few large bones.It’s stem cells transform themselves into white and red blood cells and platelets.essential for immunity and circulation
- 3. Bone marrow cells (BMCs) differentiate into various cells:hepatocytesendothelial cells of the blood vessel epithelial cells of the stomach, esophagus, small intestine, large intestine and bronchuscardiac muscle skeletal muscleneural cells
- 4. This experiment:examined whether bone marrow stem cells can differentiate into retinal neural cells in adult rats.
- 5. Experiment overview:Collection of BMC’s stem cells.Injury of Rat’s eye.Injection of BMC’s stem cellsSectioning of the eye Data AnalysisConclusion
- 6. Materials and MethodsPreparation of Stem Cell-Enriched BMCs for grafting:5-fluorouracil injected into the peritoneal cavity 4-week old male rat (inside abdominal cavity)BMCs were obtained from femurs and tibias (leg) Fractionated by density centrifugation using Lymphoprep™ density solution collected and labeled.
- 7. Materials and MethodsRats and Grafting Procedurerats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium.pupils were dilated with 0.5% tropic amide the corneas were further anesthetized with drops of 0.4% oxybuprocainehydrochlorid
- 8. Materials and MethodsInjury:eyeballs were perforated at the equator with a 30-gauge needleretina was injured by scratching (under a surgical microscope)special care was taken to injure the whole layer of the retina
- 9. Materials and MethodsPost injury: 20 μl of the cell suspension, containing 200,000 cells, were slowly injected into the intravitreous space.6 rats, 6 injected eyes with BMC’s stem cells.Control-20 μl of normal saline solution injected into the same place of injured eyes.
- 10. Materials and MethodsTissue SectioningThe animals were sacrificed 2 weeks after injectioneyes were enucleate and prepared for cutting. Samples were stained and observed under confocal microscope.
- 11. Results: BMCs had been built into the host retina in 83% of the experimental eyes (5/6). Saline treated retina showed progressing damage. BMC’s treated cells showed cell proliferation.
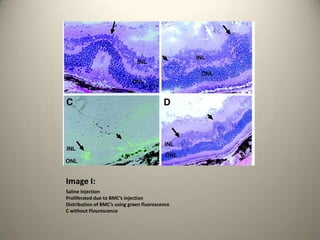
- 12. Image I:Saline injectionProliferated due to BMC’s injectionDistribution of BMC’s using green fluorescenceC without Flourescence
- 13. Image I:The grafted cells( green fluorescence) were distributed around the injured sites.Grafted cells were observed at the site of injury and at normal retinal structure.Most of the grafted cells were in the injured siteBMCs had migrated into the retina, followed by proliferation and differentiation into retinal neural cells.
- 14. Image IIImmunohistochemistry on Sections after Transplantation
- 15. Image II Injected cells labeled with expressed green fluorescence. Astrocytes, carbindin, vimentin, and rhodopsin, red fluorescence. Incorporated bone marrow-derived cells, yellow fluorescence. Incorporated bone marrow cells had differentiated into retinal cells.
- 16. Discussion:stem cell-enriched BMCs injected into injured eyes differentiated into retinal neural cells in vivo.Injection of retinal tissue of newborn and brain-derived cell lines are other methods that did not bring same results.
- 17. Conclusion: stem cell-enriched BMCs have the ability to differentiate into retinal neural cells.Injection of stem cell-enriched BMCs into the retina would help repair damaged retinal cells.
- 18. Take home message: injection of BMC’s into the eye can potentially rescue injured retinal tissue, even in humans.